Then, using cloud computing, the software explores all the possible permutations of a solution, quickly generating design alternatives. It tests and learns from each iteration what works and what doesn’t.
With generative design, there is no single solution, instead, there are potentially thousands of great solutions. You choose the design which best fits your needs.
What’s the main idea of generative design?
The idea of complete replacement of the designer by the algorithm sounds attractive and modern, but it is wrong and weakly promising. The designer helps the team to turn the raw idea into a holistic interface with good logical work, information architecture and visual style that solve business problems and strengthen the brand.
In the course of the work, it takes a huge number of decisions, many of which can not be described with clear procedures.
In addition, incoming requirements are erroneous and contradictory in separate details, so that the designer helps a manager to solve these collisions — it makes the product better.
All this is much better than choosing the right template and painting it with modern stylistics.
But if we are talking about creative partnership, when the designer, in pair with algorithms, solves product problems — there are plenty of perspectives and good examples.
Roelof Pieters and Samim Winiger study the history of computers in detail, as design assistants.
They distinguish three levels of development tools:
the first generation has translated analog instruments into programs and has developed along the path of increasing capabilities.
the second has learned to take over part of the routine operations that previously required professional expertise.
the third should become a co-author of decisions, helping to find new interesting directions.
The authors conduct a good analogy with generative art — the designer determines the algorithms by which the work is formed, and then manually selects the most successful derivatives.
If the bust is not entirely manual, the computer will also help to filter the resulting stream — the work will become even more productive and creative.
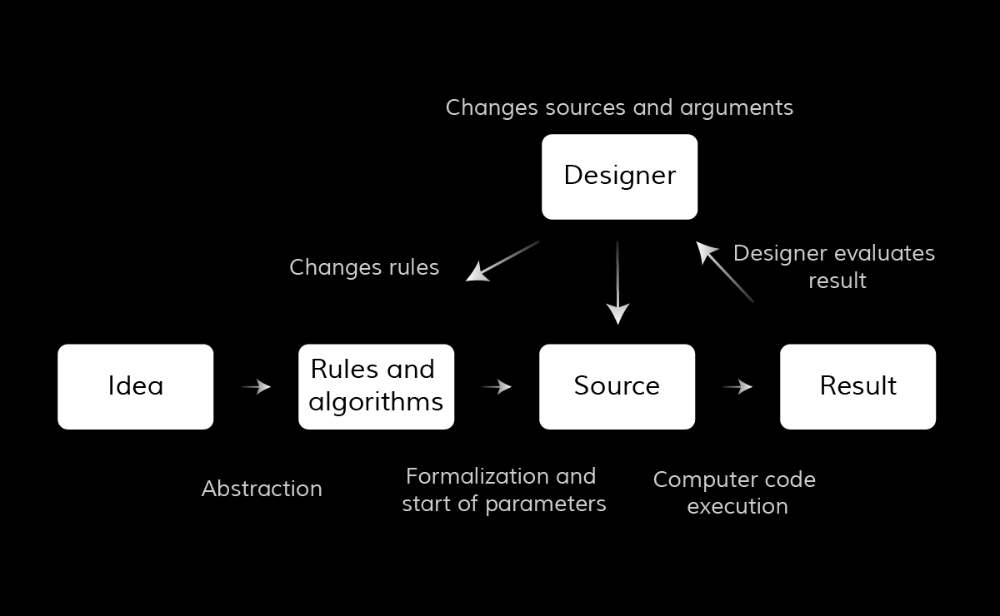
The algorithmic design should become such an “exoskeleton” for the designer, significantly increasing the number and depth of development of solutions.
How does it help?
How can the designer and computer interact in such a node? You can see the overall process of food work:
explore the space of problems and take for solutions those that will give maximum value to business and users.
explore the solution space and choose the one that best covers the problem.
generate, launch and distribute a product that solves the selected problem.
To evaluate the effectiveness of the chosen solution in practice and optimize it we need markets, segments of the target audience, business models, product types, internal organizational structures at the same time and there are so many, that universal solutions for all are just utopia.
Therefore, it should rather go about own decisions of companies, confined to specific tasks. Going down to the level of specific design solutions, it builds the interface, preparing graphics and content.
Simple publishing tools like Medium, Readymag, and Tilda have already reduced the amount of manual work — there are plenty of good templates with which you can create a good result without a designer. Improving the templates will make the entry threshold even lower.
Yes, this way does not create a revolutionary product, but you can free yourself some time for this. And we must admit that a huge part of everyday tasks is more than utilitarian and does not require revolutions. And if the company is mature and has a design system, connecting to its algorithms than it will allow you to do more with less.
For example, a designer and a developer describe the logic of processing incoming signals — content, context, user information and actions, and then the algorithm itself generates screens based on ready-made patterns and principles.
It allows you to achieve fine-tuning for a specific narrow situation or scenario without having to draw manually and develop dozens of screen states.
Creating the same type of graphics in different variations is one of the dullest parts of the designer’s work.
It takes a lot of time and demotivates, while these forces could be spent on more meaningful product work.
Absolutely black magic takes place in the direction of neural networks. One of the best examples, the Prisma application edits photos under the work of famous artists.
Will this work be selected by illustrators?
Those who have a good style are unlikely, but this, again, will reduce the threshold of the entrance to receive good-quality illustrations for an article or a site where.
But this, again, will reduce the threshold of the entrance to receive good-quality illustrations for an article or a site where the absolutely unique approach is not required. Farewell, sad stock photo!
For complex stylistics, it will help to get a quick sketch in the spirit of “what if we try to paint a building or a cat in our style.”
You can do storyboards and describe scenarios in the form of comics (photo easily turns into a sketch).
We think this list of applications will expand soon.
The story is beautiful, but we must understand that the algorithms are built according to clearly described rules, even if they are great with the help of machine learning.
The strength of the designer is that he can break these rules and ask new one, so in a year something quite different will be considered as a beautiful.
Of course, not everyone in our profession is strong and the algorithms will easily replace lazy ones. But for those who know how to both comply and break the rules, a whole new set of tools and opportunities will open up.
Main Benefits of Generative UI/UX Design

How does generative design help improve UX design services? Here are just a few of the top benefits.
UX designers can use this to optimize the process
Generative design uses advanced algorithms and cloud computing to rapidly explore multiple design permutations. This automation of creating alternatives allows you to speed up and diversify the UX design process.
In other words, you can get several different options and ideas. Further, they can be used and improved for a better final result, as well as for user research and usability testing.
Time savings
Gen design can significantly reduce the time required to develop design solutions. For example, UX designers must create an optimal layout for a new mobile application. Simply specifying parameters such as functionality, color range, accessibility, etc., is enough, and the software creates hundreds of viable layouts in a short time. A person would need many times more resources and hours for this.
This is not necessarily professional UX design, but combined with manual intervention, you can quickly narrow down the best options and focus on refining the final design. This saves you weeks of manual work.
Overall efficiency
Those who have been providing UX design services for a long time know that it is very important to be able to set priorities correctly. This applies not only to the overall user experience but also to details such as the application’s primary features.
The AI gene in UX design helps to effectively prioritize tasks, stages of development, list of features, etc. All this in a complex allows you to create a high-tech application faster and better without spending a lot of time on manual work and experiments.
Innovation
Generative UX design brings innovation to the table when it comes to exploring unconventional solutions that may not be immediately obvious to designers. It can direct the UX design process in a more future-proof direction, find ways to solve non-obvious flaws and offer fresher solutions.
In combination with a creative approach and the skills of UX designers, this allows you to create a new product completely tailored to the requirements of the end user, but with an eye on the future.
Challenges and Limitations of Generative Design
While generative design offers numerous benefits, it also has its challenges and limitations that cannot be ignored. Let’s take a closer look at a few potential drawbacks to consider.
Excessive dependence on algorithms
This is one of the main risks of generative design. This can lead to lacking human contact and creativity.
Such solutions are often technically sound but do not resonate with users on an emotional or aesthetic level. An over-reliance on technology can also stifle a designer’s intuitive problem-solving abilities, which are often critical to creating truly innovative products.
Limited creativity
Algorithms work on the basis of predefined rules and input data. They can create a huge number of designs, but they cannot always come up with truly innovative or unique solutions.
Human creativity, which often thrives on breaking the rules and thinking outside the box, is necessary for innovative design services. Generative design often produces similar results, where variation is incremental rather than transformative. This potentially limits the exploration of radically new concepts.
Complex learning curve
Generative design tools can be complex and require a significant amount of time and effort to learn. Designers must understand both the software and the principles of generative design in order to use them effectively. Not to mention that all this must be supported by human experience in order to work harmoniously.
This learning curve can be a barrier for some professionals, especially those more accustomed to traditional design methods. Complexity can also lead to errors if not properly managed, requiring a combination of technical and design expertise.
Quality of input data
Obviously, the quality of the output data largely depends on the quality of the input data. It is relevant both for UX design and usability testing. Inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to suboptimal design decisions.
Providing high-quality, comprehensive input is critical but can be challenging. This means that in the early stages of a project, significant resources may be required to collect and verify data. This is a rather time-consuming process.
In addition, algorithms are not immune to biases present in their training data. If the data used is biased, the final designs may also be biased. This can lead to ethical issues, especially in apps where accuracy and inclusiveness are important.
For example, generative design services used in public infrastructure must take into account the diverse needs of users; otherwise, it risks maintaining existing inequality.
Read more on proper design services here.
Lack of context understanding
Algorithms lack the ability to understand context the way humans do. They can create designs that are technically correct but contextually inappropriate.
Human supervision is necessary to ensure that structures are fit for their intended use and adapted to the environment. A lack of context awareness means that your product doesn’t properly take into account practical constraints or user behavior. This, in turn, results in significant functionality and accessibility issues.
Difficulties in integrating with existing work processes
Integrating generative design tools into existing workflows can be challenging. This can require significant changes in processes and collaboration methods, which can be disruptive and time-consuming.
Existing team dynamics and project management practices may need to be adapted to accommodate these new tools. You may encounter resistance, and your team will need ongoing training and support.
Cost and availability
Advanced generative design tools can be expensive and not available to all organizations, especially small ones. This can make a difference in who can benefit from these advanced technologies.
The high cost of implementation includes not only the software itself but also the hardware required to run complex algorithms and the potential need for specialized personnel to manage and operate these tools.
Also, designs created by algorithms still need to be thoroughly tested. This is critical to ensure that they meet the required standards and perform well in real-world conditions.
This means that the generative design process does not eliminate the need for user research, prototyping, and testing phases, which can still be resource-intensive.
Acceptance by users
End users may experience skepticism or resistance when it comes to algorithm-generated designs. This is especially true in industries where traditional craftsmanship and the human touch are highly valued.
Therefore, convincing stakeholders of the validity and reliability of generative projects may require additional efforts and evidence of success. It is much easier to work with a team of designers.
Dependence on technology
More reliance on technology can lead to a decline in traditional design skills among professionals. As the industry moves towards more automated processes, there is a risk that basic design skills may be neglected, potentially affecting the quality of design education and training.
In other words, while generative design is a powerful tool, it is not without challenges. To achieve the best results, designers must balance the use of algorithms with human creativity and judgment. Recognizing and addressing these limitations is essential to realizing the full potential of generative design.
By understanding these challenges, you can better prepare to integrate generative design into your workflows, ensuring a harmonious blend of human and machine intelligence.
Future Trends in Generative Design

Let’s take a look at how gen design can transform UX design services.
Integration of AI and Machine Learning
The integration of advanced AI and machine learning algorithms into generative UX design is revolutionizing the field. These technologies will allow the software to learn from past developments and improve over time.
Thus, generative design tools become smarter and more efficient. Accordingly, UX design services are becoming more innovative and optimized.
AI is becoming an important part of the UX design process, if not in terms of creativity, then in terms of testing ideas and user testing. Specialists can develop highly specialized and adaptive designs that meet the specific needs and preferences of users.
Real-time сollaboration
Many generative design tools already support real-time collaboration. In the future, it will become an unconditional component. such software.
This way, UX designers, engineers and other stakeholders can seamlessly work together from different locations. The enhanced capabilities of cloud computing facilitate this collaborative approach, enabling instant sharing and iteration of design concepts. All this will develop together in the field of user experience design services.
This trend breaks down geographical barriers and promotes a more collaborative and inclusive design process. Teams at top design companies can bring their diverse experiences and ideas to bear, resulting in more innovative and comprehensive designs. Real-time collaboration can streamline the digital product development process, reducing delays and improving project outcomes.
Cross-disciplinary applications
Generative design transcends the traditional realms of UX design, finding applications in a wide range of industries such as healthcare, automotive, aerospace, and fashion. For example, in healthcare, generative UX design can be used to create custom medical implants that perfectly fit the patient’s anatomy. This greatly simplifies the work of medical workers and improves the results of treatment.
The interdisciplinary application of generative design will stimulate innovation and efficiency in various design services. The analysis of different experiences from different disciplines and the combination of different techniques stimulate a creative approach and an extraordinary solution. This especially applies to the search for tools to develop universal user interfaces.
Sustainability and eco-friendly designs
Future generative UX design tools will increasingly focus on sustainability. They optimize designs to minimize waste and energy consumption by using environmentally friendly materials and processes. Artificial intelligence algorithms will help determine the most sustainable solutions for the UX design process, which at the same time meet functional requirements.
This trend will greatly contribute to global efforts towards sustainable development. In architecture, buildings designed with generative design tools use resources more efficiently and will have less impact on the environment. In product design, companies will be able to create environmentally friendly products that appeal to environmentally conscious consumers, enhancing their brand reputation and market competitiveness.
Indeed, this approach is also relevant in the field of digital design services. Generative design is about finding ecological solutions and more efficient ways of accomplishing tasks.
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) integration
Generative design tools will increasingly integrate with AR and VR technologies. It will help UX design professionals visualize and interact with their creations in immersive environments. It also helps to more intuitively explore and manipulate complex projects, improving the design process, user testing, communication with stakeholders, and design services in general.
In the field of architecture and interior design, clients can virtually walk through the space and experience it even before construction begins. This way, the team can gather valuable feedback that can be incorporated into the design.
In product design, virtual reality simulations can help designers understand how a product will function and look in the real world. Customers can decide whether to hire this design team for product app development. This definitely leads to better design solutions and fewer expensive prototypes.
Hyper-personalization
Generative UX design will provide hyper-personalization. It allows you to adapt products and experiences to the preferences and needs of individual users.
Generative design algorithms can create customized solutions that meet specific requirements by analyzing data and user behavior. This is an ultra-fast and ultra-effective tool for user research.
In a digital experience, websites and apps can dynamically adjust their interfaces to optimize usability and engagement for each user. This trend will increase user satisfaction and loyalty by providing highly relevant and personalized experiences from design services.
Collaborative Human-AI design teams
Experts predict a shift toward greater collaboration between humans and artificial intelligence in the future. UX designers will work together with artificial intelligence to increase creativity and innovation. These teams will leverage the strengths of both human intuition and machine efficiency to produce superior results and expand the range of their design services.
In addition, during product development, joint human-AI teams can accelerate the innovation process by combining designers’ creative ideas with artificial intelligence’s computing power. It’s also about exploring a wider range of UX design possibilities.
This synergy will lead to more innovative and effective solutions in various industries. It will also allow companies to take a new look at unique UX design services and choose those who know how to combine their own creativity with AI capabilities.
Real-time feedback and iteration
Generative design tools will increasingly offer real-time feedback and iterative capabilities. This will help UX design service providers make immediate adjustments based on performance metrics and user feedback.
Such an approach to user testing and immediate feedback also helps to significantly shorten the design cycle, better prioritize the necessary design services. As a result, such an approach improves the quality of the final product.
In software and application development, real-time iteration can lead to more user-friendly interfaces and a better overall user experience. In engineering, this can help quickly identify and eliminate design flaws, creating more robust, sustainable, and reliable products.
The future of generative design is incredibly promising. It applies not only to UX design, but also to the work of software developers.
Advances in artificial intelligence and a new approach to immediate interaction with the user are changing the design field. These trends will not only improve the industry but will also have far-reaching effects on various other sectors, promoting innovation, innovative solutions, efficiency, and sustainability.
The Role of Designer in Generative Design

Although generative design uses advanced algorithms to create multiple design options, the role of humans in providing UX design services remains crucial. Here are the main reasons why this is so.
Human creativity really matters
This applies to everyone: designers, software developers, marketers, etc. Algorithms can create many opportunities for UX design, but they still cannot replace human creativity. Humans offer unique ideas and artistic visions that machines cannot reproduce. They understand the nuances of aesthetics, brand identity, and user research, which are important for professional design services.
Decision-making skills are critical
Humans are essential in evaluating and selecting the best design options generated by algorithms. They consider factors such as functionality, usability, and visual appeal, and they make informed decisions based on their experience and intuition.
Human judgment ensures that the end result meets the specific needs and preferences of the target audience. It is the person who is able to make flexible decisions.
Humans have the ability to solve problems
Algorithms are just algorithms. They can be a problem-solving tool but not a solution.
Unanticipated issues and complex problems often arise during the design process. Designers are great at solving these obstacles and can adapt their approach to overcome them. Their ability to think critically and creatively is vital to improving generative design outcomes.
Instead of seeing algorithms as replacements, people should see them as powerful tools that empower them. Using the strengths of generative design, you can quickly explore a wide range of options, save time on repetitive tasks and focus on more strategic and creative aspects of the project.
A balance of innovation and practicality
Developers strike a balance between innovative solutions proposed by algorithms and practical considerations such as feasibility, cost, industry specifics (fintech app design differs from healthcare), and user requirements. They ensure that the final design is not only creative but also functional and viable for implementation.
Thus, although generative design technology greatly improves the design process, the human role remains indispensable.
Wrapping Up
So, generative design is a part of significant progress. This offers the potential to rapidly explore a wide range of design solutions using the power of algorithms and cloud computing. In addition, it increases efficiency, promotes innovation and can significantly reduce the time required to develop optimal design solutions.
However, it is very important to be aware of and address the challenges and limitations associated with this technology. Over-reliance on algorithms, complexity of tools, ethical considerations, and the need for high-quality data are just some of the challenges that need to be managed.
To truly harness the power of generative design, a balanced approach is essential. It involves combining the computational power of algorithms with the creativity, intuition, and understanding of the context that human designers bring to the table.
In doing so, we can ensure that we have a valuable tool in our hands that enhances, rather than replaces, the human element in the design process. Moving forward, the integration of generative design with human experience is likely to lead to even more innovative and effective design solutions, ultimately driving advancements across industries.










