When it comes to necessary technical changes in business, system integration is an absolute must. Many organizations cite integration challenges as a major hurdle in their digital transformation journey.
For tech leaders in healthcare and insurance, this is especially true as they navigate critical issues like data security, efficiency, and interoperability. Healthcare providers often struggle with disconnected patient records, while insurers face headaches syncing claims systems. Add to that the pressure on IT teams to deliver seamless integrations faster than ever – it’s clear this is no small task.
At Cadabra Studio, we’ve seen the transformative power of system integration firsthand. From reducing inefficiencies to staying compliant with regulations, effective integration can revolutionize operations in industries where every second and detail counts.
So, I’ve created this guide to help you understand all the peculiarities of system integrations. It breaks down the essentials:
- Main types and methods of integration.
- Real value and benefits, as well as challenges you may face.
- The best practices and trends.
- Actionable insights to help you get started.
What is System Integration?
System integration is the process of connecting various software applications, hardware, or operational processes to function as a unified system. At its core, system integration bridges the gaps between disparate components, enabling them to communicate and work together seamlessly.
Technically, this involves designing and implementing solutions like architectures, middleware, and APIs to facilitate efficient and error-free data exchange. Illustrative examples are integrating an electronic health record (EHR) system with patient appointment scheduling or connecting insurance claim processing systems with analytics platforms.
Global system integration market overview
According to recent research, the global system integration market is on a rapid growth trajectory, valued at more than $516 billion in 2024 and expected to reach $1,946.37 billion by 2034. North America leads the market, contributing over 36% of global revenue in 2023, with the U.S. projected to grow from more than $130.23 billion in 2024 to $500 billion by 2034.
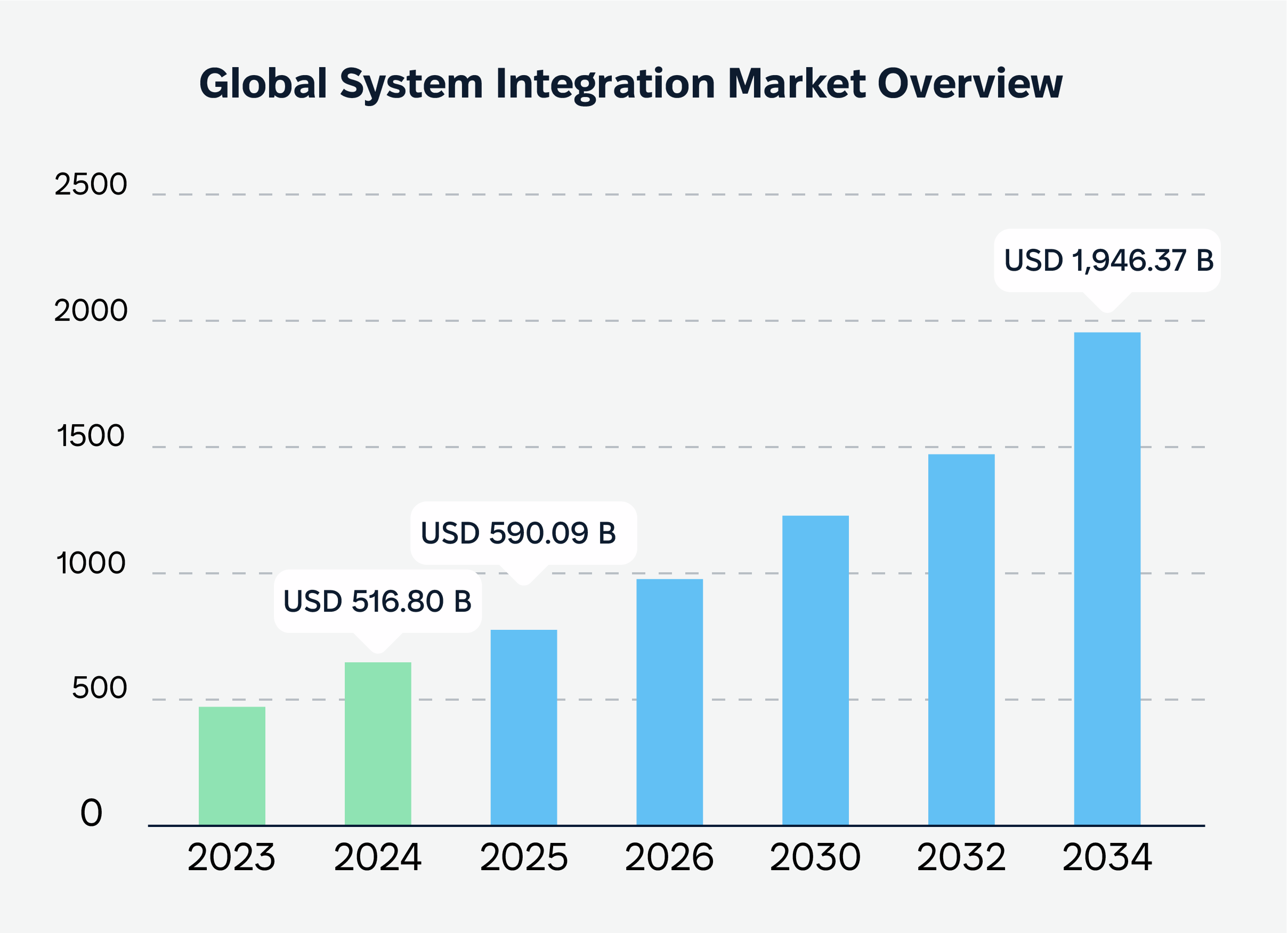
The banking, financial services, and insurance (BFSI) sector held the largest market share in 2023, driven by digital transformation initiatives, fintech growth, and rising demand for secure, efficient banking operations. Other notable sectors include healthcare, defense & security, and IT & telecom.
Challenges such as high initial automation costs persist, but opportunities like IT/OT convergence and virtualization software solutions are paving the way for innovation. The hardware integration segment dominates due to advancements in wireless technologies, while augmented and virtual reality, combined with 5G, are further boosting industrial automation demand.
The business value behind the system integration
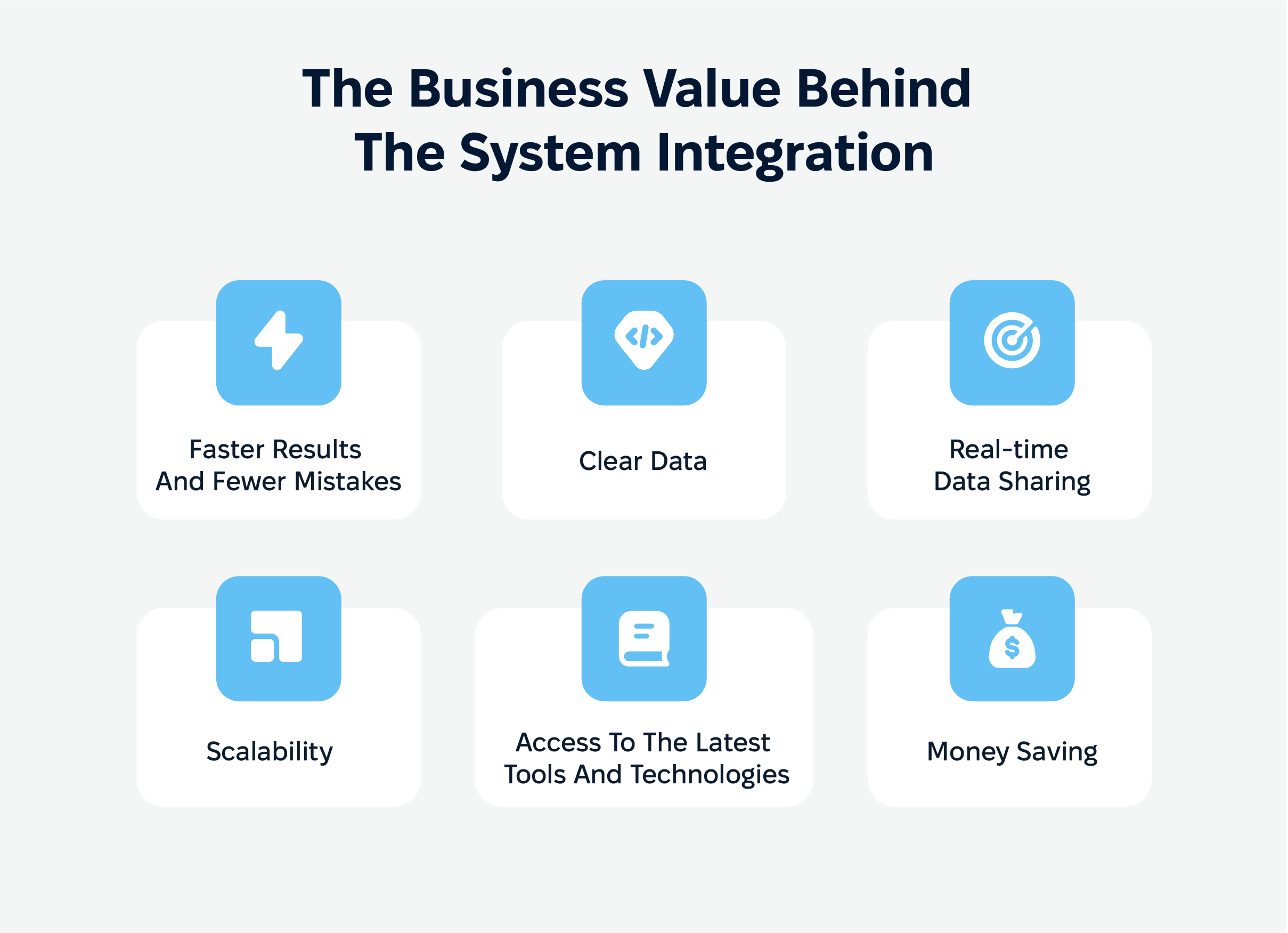
- Work smarter, not harder
Integrated systems cut out the repetitive stuff, automate workflows, and keep things moving like a well-oiled machine. That means faster results and fewer mistakes.
- Clear data
Real-time data sharing keeps everyone on the same page with accurate, up-to-the-minute info. No more guessing games or dealing with conflicting numbers.
- Room to grow
Integrated platforms open doors to the latest tools and tech, making it easier to scale up and roll with whatever the future throws at you.
- Money saving
By streamlining business processes, and making the most of your resources, you’ll cut costs while boosting productivity. It’s like killing two birds with one stone.
Current Industry Challenges
Despite its importance, system integration poses several challenges:
Interoperability issues. Legacy systems often lack compatibility with modern solutions, making integration complex and time-consuming.
Data security risks. With the rise in cyber threats, ensuring secure data transmission and storage becomes a critical concern, especially in industries like healthcare and insurance, where data sensitivity is paramount.
Regulatory compliance. Adhering to regulations such as HIPAA in healthcare or GDPR for data protection adds complexity to integration efforts. A failure in these areas could result in costly data breaches, loss of trust, and legal penalties.
Resource constraints. Integration projects demand technical expertise, time, and financial resources. Many organizations struggle to allocate these adequately.
Healthcare/Insurance-specific integration challenges
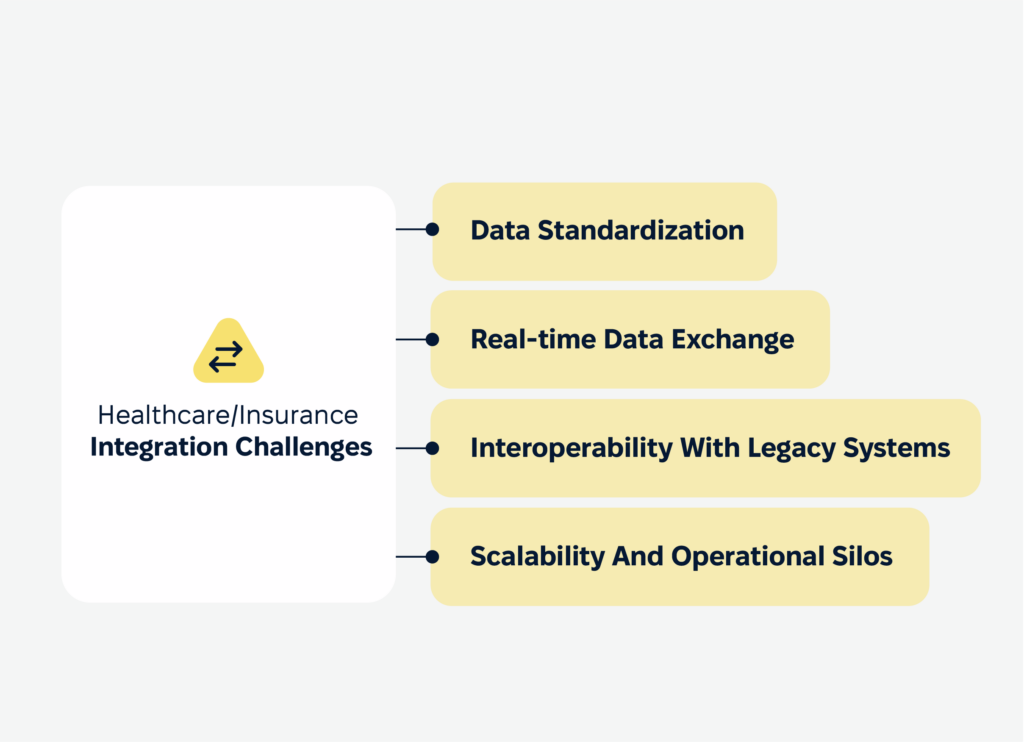
Healthcare and insurance industries face significant challenges in system integration due to the complexity of their operations and the critical nature of the data they handle.
- A major issue is interoperability with legacy systems, which often lack APIs and use outdated formats, making integration costly and time-consuming.
- These industries struggle with data standardization, as diverse formats and terminologies (e.g., ICD-10 codes versus custom claim forms) complicate seamless communication across systems.
- Scalability and operational silos further hinder integration efforts. Healthcare providers must manage the explosion of telehealth data while insurers face surges during crises. Both industries also grapple with organizational silos and resistance to change, where teams accustomed to legacy workflows may resist adopting integrated systems.
- Real-time data exchange is critical but challenging, especially for processes like syncing patient records or insurance claims. Delays or errors in real-time updates can harm patient outcomes or frustrate policyholders.
Get Your Free Consultation
Our experts will analyze your integration needs and discuss a roadmap
Types of System Integration
Horizontal integration
Horizontal integration is like connecting the dots within the same layer of your operation. It brings together subsystems doing similar tasks to create a smooth, streamlined workflow.
Pros:
- Cuts out unnecessary steps and makes things easier to manage.
- Perfect for merging systems with the same job description.
Cons:
- Doesn’t play well with growing complexity—it’s not built to scale.
- Sticks to one layer of operations, so it’s not ideal if you need more interconnectedness.
The perfect example is linking up appointment scheduling software with electronic health records (EHRs). It simplifies admin work and keeps things running without a hitch. For healthcare providers, getting multiple systems on the same page improves patient care and cuts down on errors. This is one of the types of system integration that is smoothing out workflows.
Vertical integration
Vertical integration takes things a step further, connecting systems across different levels. It’s about ensuring data flows seamlessly from the ground up, all the way to decision-making tools.
Pros:
- Covers the full process, making things run end-to-end without a snag.
- Helps with smarter decision-making since everything’s tied together.
Cons:
- Costs can add up quickly, and implementation can feel like climbing a mountain.
- A hiccup during setup can cause some headaches.
An example is linking claims systems with analytics platforms to pull out insights that are worth their weight in gold. This type of integration shines when transparency and efficiency are top priorities. Just be ready to jump through some regulatory hoops (think HIPAA or GDPR).
Star integration (Point-to-Point)
Star integration, or point-to-point, is the OG of types of system integration. It directly connects systems one by one, like building a web.
Pros:
- Quick and easy to set up, especially for smaller operations.
- Doesn’t cost an arm and a leg upfront.
Cons:
- As you add more systems, things can spiral into what we call “spaghetti architecture.” Messy, hard to maintain, and not great for scaling.
- Keeping it all up and running gets trickier with each new connection.
For instance, a pharmacy database can be hooked directly to a billing system via APIs. It works fine – until you try to scale up. This is a go-to for older, legacy systems in healthcare and insurance. But if you’re thinking big, you’ll outgrow it pretty fast.
Enterprise service bus (ESB)
Now we’re talking about ESB, the heavyweight champion of enterprise application integration. This method uses middleware as a central hub, allowing all your systems to talk to each other through one streamlined platform.
Pros:
- Built for large, complex setups—it can handle the big leagues.
- Centralized control makes managing data flow a breeze.
Cons:
- Not cheap to set up, and it takes time to get off the ground.
- Middleware maintenance can feel like babysitting.
An insurance company, for instance, can use ESB as one of the proper types of system integration to sync underwriting, policy management, and claims processing. If you’re in healthcare or insurance and juggling a lot of disparate systems, ESB is your best bet. It’s built for complexity and compliance, but be ready to invest time and resources.
Types of System Integration
| Integration Type | Scalability | Complexity | Use Case Example | Industry Insight |
| Horizontal Integration | Low | Moderate | Linking appointment scheduling with EHRs in healthcare. | Best for consolidating similar systems at the same level. |
| Vertical Integration | High | High | Claims systems integrated with analytics platforms. | Enables end-to-end workflows for better decision-making. |
| Star Integration | Low to Medium | Low to High | API connections between pharmacy databases and billing. | Suitable for smaller setups but challenging to scale. |
| Enterprise Service Bus | Very High | Very High | Middleware for insurer systems (e.g., claims, policies). | Ideal for large-scale operations with complex ecosystems. |
System Integration Methods
A proper integration method balances your operational needs, scalability plans, and resources. Here’s a closer look at the main approaches, complete with methodologies, factors to weigh, and real-world examples to bring it all home.
Point-to-point integration
Point-to-point is the “plug-and-play” of system integration methods and is a simple, direct connection between two systems.
How it works: Systems connect via APIs, custom scripts, or specific data protocols. Each connection is tailored to fit the data format and communication needs of the two systems.
What to consider:
- Great for smaller setups with only a handful of systems.
- Requires manual development and upkeep for each connection.
- Doesn’t scale well – things can get messy fast as connections grow.
What makes it work: Well-documented APIs and data protocols and rigorous testing to ensure smooth system communication.
Watch out for:
- Spaghetti Syndrome: too many connections turn into a tangled mess, making maintenance a nightmare.
- Constant fixes: a tweak in one system can break others, adding to the upkeep load.
Middleware-based integration
Middleware is like the traffic cop of system integration methods. It routes data between different systems, all from a central hub.
How it works: Middleware provides a standardized platform for system communication, cutting out the need for direct connections.
What to consider:
- Initial setup can be complex and requires technical expertise.
- It’s an investment – middleware platforms don’t come cheap.
What makes it work: Planning is crucial to ensure the middleware aligns with your workflows and scalable architecture ensures you’re future-proofed. IT teams need proper training to handle the platform.
Watch out for:
- The upfront cost of middleware can be steep.
- If the middleware goes down, everything connected to it does, too.
Cloud-based integration
Cloud-based hybrid integration platforms leverage iPaaS ( platform-as-a-service system integration methods) tools to connect systems, especially in hybrid or fully cloud environments.
How it works: Tools like Azure Logic Apps, Dell Boomi, or AWS AppFlow handle real-time data exchange. Ideal for setups mixing cloud-based and on-premise systems.
What to consider:
- Suits organizations with a “cloud-first” strategy.
- Requires a robust network to avoid hiccups in connectivity.
- Security and compliance are non-negotiable for sensitive data.
What makes it work: Choose a cloud provider offering the right integration tools. Implement advanced security measures like encryption and multi-factor authentication.
Watch out for:
- Data in transit is vulnerable without proper safeguards.
- Relying heavily on one cloud provider might limit your options down the line.
Third-party integration platforms
These platforms are the fast-track option, offering pre-built connectors to get systems talking with minimal coding.
How it works: Platforms like MuleSoft, Zapier, or Workato provide plug-and-play connectors for common integrations.
What to consider:
- Great for quick deployment with minimal technical effort.
- Limited customization may pose challenges for unique workflows.
What makes it work: Take advantage of pre-built connectors to save time. Opt for platforms with strong support and detailed documentation.
Watch out for:
- Pre-built solutions might not fit your exact needs, especially flexibility.
- Monthly fees can add up over time.
Integration Method | Pros | Cons |
Point-to-Point | – Simple, direct connections. – Quick implementation for small systems. | – Poor scalability; connections grow messy as systems increase. – High maintenance with frequent fixes. |
Middleware-Based | – Centralized control simplifies data routing. – Scalable for future needs. | – High upfront costs. – Middleware failure impacts all connected systems. |
Cloud-Based Integration | – Ideal for cloud-first or hybrid setups. – Supports real-time data exchange. | – Data vulnerabilities during transfer. – Dependency on cloud provider limits flexibility. |
Third-Party Platforms | – Quick deployment with minimal coding. – Pre-built connectors save time and effort. | – Limited customization for unique needs. – Ongoing subscription fees add to long-term costs. |
Project Lifecycle: System Integration Guide
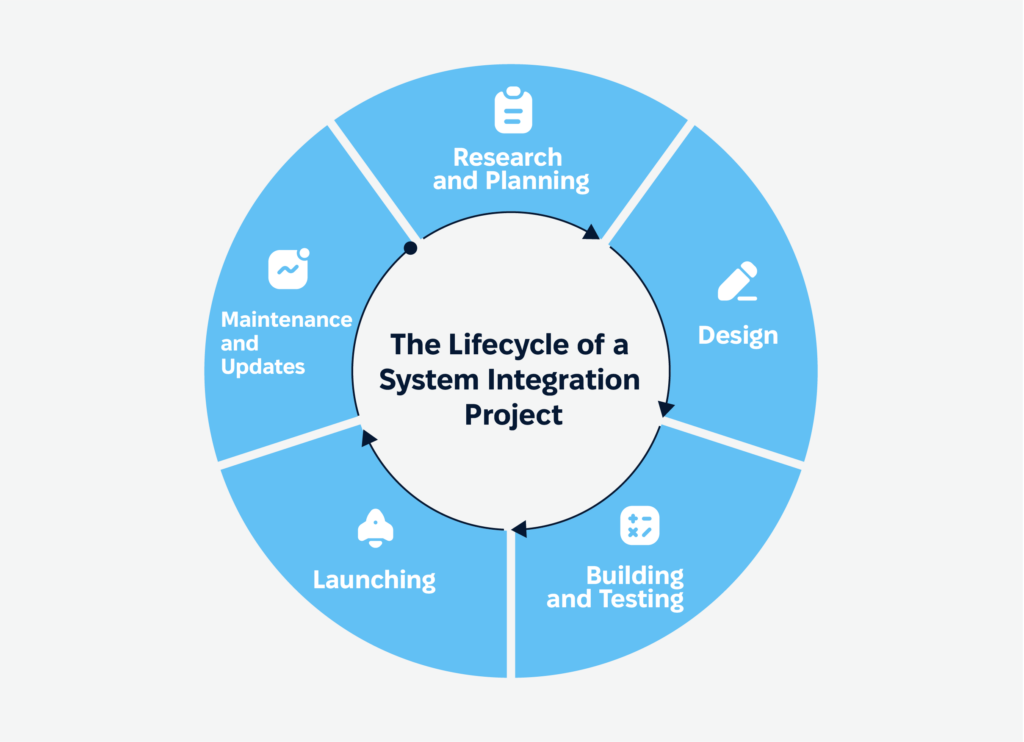
Every integration project is a journey, and knowing the roadmap can save you headaches. Here’s a simple breakdown:
1. Research and planning. Lay the groundwork: What are your goals? What’s your budget? What’s your timeline?
Tip: Get input from everyone who’ll use the system – don’t leave key players out of the loop.
2. Designing the blueprint. Decide how the systems will connect. Will you use middleware, APIs, or direct integration?
Tip: Future-proof your design so it can handle growth and new technologies down the road.
3. Building and testing. Start the integration work and test, test, test. Fixing issues early saves a ton of headaches later.
Tip: Begin with a pilot phase before going all-in. It’s like dipping your toes in the water before diving.
4. Go live. Roll it out! Just make sure to have a backup plan in case things go sideways.
Tip: Train your team thoroughly so they hit the ground running.
5. Maintenance and updates. Even after launch, monitor the system regularly to catch problems before they snowball.
Tip: Use KPIs like uptime, speed, or error rates to measure success.
Best Practices for System Integration
System integration is like solving a puzzle – you need the right pieces, placed strategically, to get the full picture. By combining technical expertise with organizational teamwork, businesses can make sure their system integration projects hit the mark. Here’s our system integration guide on how to do it right.
1. Start with clear objectives
Know your “why” before you start connecting systems. Whether you’re aiming to cut down on manual data entry, speed up claims processing, or improve patient care, having clear goals keeps everyone on the same page.
2. Invest in scalable solutions
Think long-term. Systems in industries like healthcare and insurance don’t just grow – they explode. Picking integration methods that can scale with your needs saves headaches down the road.
3. Prioritize data security and compliance
Encryption, secure APIs, and strict access controls are non-negotiable. Don’t forget to stay compliant with regulations like HIPAA, GDPR, or ISO 27001 – they’re not just rules; they’re trust builders. Make security audits and compliance checks part of the integration process from start to finish.
4. Leverage agile methodologies
Forget the “big bang” approach – agile is the way to go. Breaking the integration into small, testable chunks (a.k.a. sprints) lets you deliver results faster, find problems earlier, and adapt to changes without derailing the whole project.
Focus each sprint on specific systems or workflows. This keeps progress visible, stakeholders happy, and risks manageable.
5. Engage cross-functional teams
Bringing in people from IT, operations, and business units ensures that what’s being built actually meets the organization’s needs. Appoint “integration champions” from each department. These folks can provide feedback, keep their teams in the loop, and help troubleshoot issues as they arise.
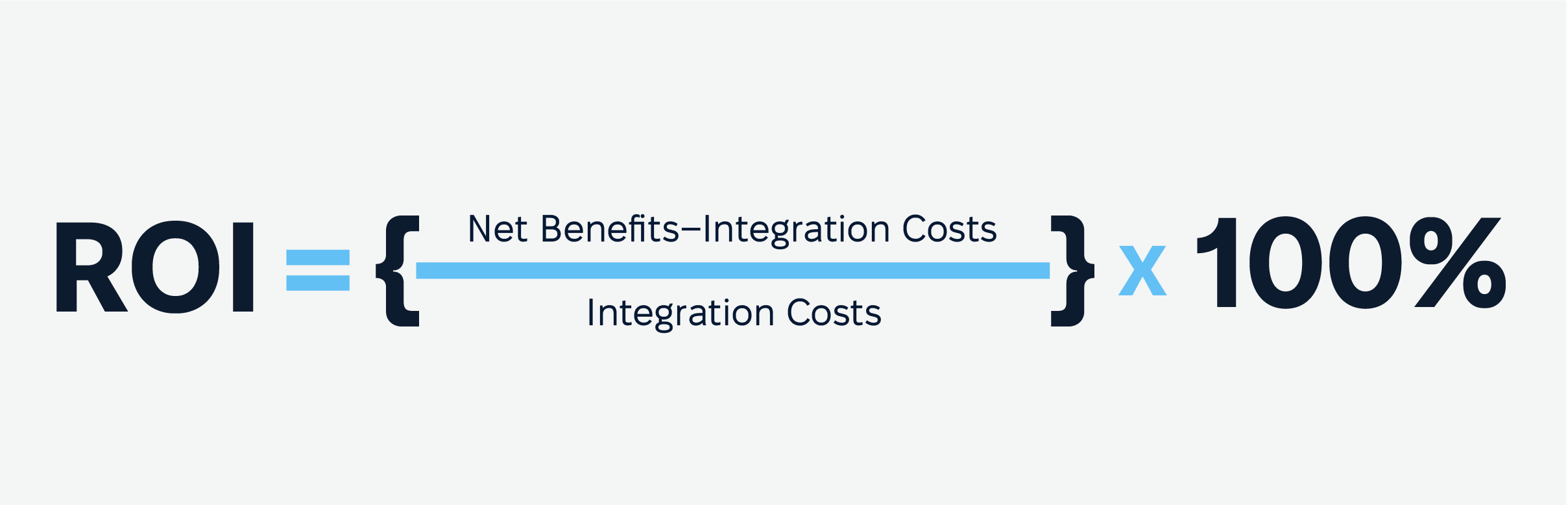
The ROI of System Integration
When done right, system integration pays off big time. Here’s how you can see (and measure) the benefits integrating systems have:
- Saving money. Automation, for instance, trims down labor costs and wipes out inefficiencies.
- Boosting efficiency. Faster claims processing, easier patient data access – it all adds up to happier customers and employees.
- Driving revenue. Better customer experiences mean more loyalty, more referrals, and, ultimately, more revenue.
- Avoiding fines and headaches. Automated compliance keeps you out of trouble with regulators.
Conclusion
System integration may seem like just about connecting the dots, but in reality, it’s the secret sauce for improving efficiency, enhancing data accuracy, and creating seamless workflows. For industries like healthcare and insurance, where data sensitivity, compliance requirements, and legacy systems are everyday hurdles, systems integration is the key to staying ahead of the curve.
By carefully choosing the right approach and leveraging the right methodologies, organizations can break down silos and streamline operations. Each method has its own pros and cons, so aligning your integration strategy with your unique needs and growth plans is critical for success.
Best practices make all the difference. Setting clear objectives, focusing on scalability, prioritizing data security, adopting agile methodologies, and fostering collaboration across departments are the building blocks of a successful integration project. These steps are especially vital in healthcare and insurance, where compliance with regulations like HIPAA, GDPR, and PCI DSS is non-negotiable.
At Cadabra Studio, we get it: system integration in industries like healthcare and insurance comes with unique challenges. Our team of experts specializes in designing tailored, secure, and scalable solutions that not only meet today’s needs but also prepare you for tomorrow’s growth. Whether you’re looking to streamline workflows, unlock deeper data insights, keep operational costs, or ensure airtight compliance, we’re here to help you every step of the way.
Ready to take your systems to the next level? Let us be your go-to partner for tackling integration challenges and unlocking the full potential of your operations. Reach out to us today, and let’s build a future where your systems work smarter, your data flows seamlessly, and your business thrives with confidence.